
Do you know what sucks when browsing a website?
Getting a 404 page.
It doesn’t matter if they mistyped the URL or the page no longer exists. 404 errors can seriously harm your brand and negatively impact your SEO by making it harder for search engines to crawl your site.
That means finding and fixing 404 errors needs to be a priority.
In this post, I’ll cover everything you need to know about 404s, why they are bad for business, how to find them, and how to fix them.
What Is a 404 Error?
A 404 error is a code that indicates a requested page cannot be found.
Whenever a page loads in a browser, it has a response status code in the HTTP header that usually isn’t visible to viewers. These responses are grouped into five categories:
- 100-199 are informational responses
- 200-299 are success responses
- 300-399 denote redirects
- 400-499 denote client errors
- 500-599 denote server errors
So what exactly does a 404 error mean?
A 404 error (also known as an HTTP 404 or 404 code) is a very specific type of client error. It means the page the viewer is trying to reach can’t be found on the server.
Hard 404 vs. Soft 404 Errors
There are actually two types of 404 errors you need to watch out for.
While you’ll have probably come across a hard 404 request when browsing a website at some point, you’re unlikely to see a soft 404 error unless you get notified by Google Search Console.
A soft 404 happens when a non-existent page on your site displays a “not found” message to users but returns a 200 OK status to search engines.
This tells Google and other search engines there’s a page at that URL. As a result, crawlers waste time trying to crawl and rank the URL.
Here’s the thing: Google is pretty good at identifying these false pages.
When it finds a page returning a 200 OK status with all the attributes of a page that should return a 404 code, it slaps a soft 404 error on it and notifies the site owner in Google Search Console.
What You Need to Know About Your Site’s 404 Errors
Okay, so you know what these errors are. Now you need to understand what causes 404 errors.
There could be many reasons why your site is returning 404 errors.
You’ll get 404 errors if you’ve deleted or removed pages from your site recently without redirecting their URLs.
404 errors can also occur if you’ve relaunched or transferred your domain and failed to redirect all your old URLs to the new site.
Sometimes 404 errors can be the result of changing a page’s URL. Altering any part of the URL, whether that’s a category name or the page’s slug, will result in a 404 error.
Even mistyping a URL in an internal link can result in a 404 page and a broken link.
Why Are 404 Errors Bad for Websites?
A large number of 404 errors could spell big trouble for your website.
Let’s start with the user’s viewpoint. Continually running into 404 errors when browsing your site will result in a terrible user experience.
Even finding one 404 error can be enough to send a visitor packing.
Read that again: just one 404 error could cost you a customer.
It gets worse, because 404 errors can also damage your rankings.
404 errors aren’t a ranking factor per se, and Google won’t penalize you directly for having lots of them.
But they can harm your SEO.
The more broken links your site has, the harder it will be for Google and other search engines to crawl your site. Link equity won’t be passed around your site well, either.
Both of these can cause a drop in rankings.
You may also suffer from high bounce rates if users leave your site after landing on a 404 page. Unlike 404 errors, bounce rates are a ranking factor, and Google could penalize your site if its bounce rate is too high.
How to Find and Fix 404 Errors on Your Site
Now you know how bad 404 errors are, let’s look at how we can find them and fix them.
Finding 404 Errors
Site crawlers like Screaming Frog are a great way to find broken links that lead to 404 errors quickly. Screaming Frog is also free if your site has 500 URLs or less.
Start by running a site audit.
Then click on Response Codes in the top menu.
Filter for Client Error 4XX to get a list of every page returning a 404 error.
Site crawlers won’t give you a complete list of 404 errors, however, as they only show broken links.
But you can find every 404 error on Google Search Console.
Google Search Console provides a list of every 404 error Googlebot finds on your site. This includes both hard 404s and soft 404s.
Login to the Search Console, click Coverage, and select the Excluded tab.
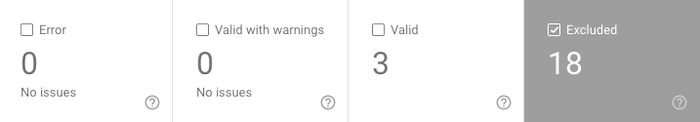
You’ll see a list of hard 404 errors marked Not found (404) and soft 404 errors marked Soft 404.
Click on each to see a full list of pages returning 404 errors.
You can also find 404 errors in Bing Webmaster Tools by clicking Reports & Data and then Crawl Information.
Finally, you can find 404 errors using my SEO tool, Ubersuggest.
Head to the site audit tab in the left-hand sidebar.

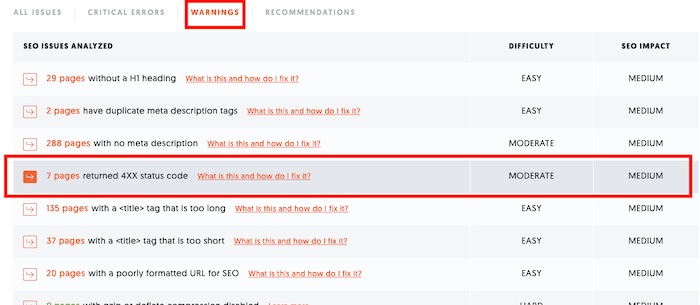
Run a Site Audit and then click Critical Errors.
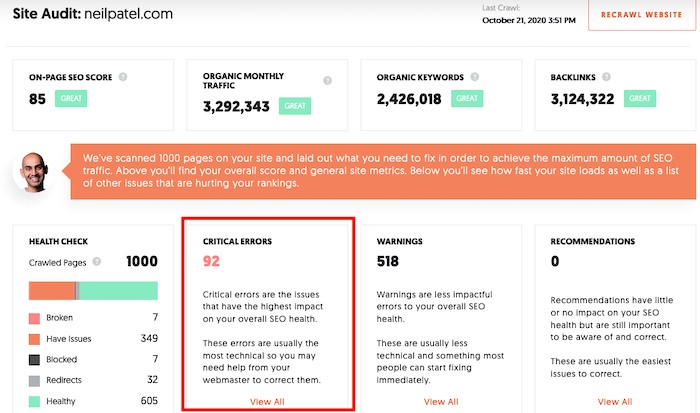
Then click on the Warnings tab at the top of the page.
If any pages return 404 error codes, they’ll be listed here. Click on the issue to see a full list of the pages.
Fix 404 Errors
Now it’s time to fix all the errors you’ve found.
Here are four ways to do it:
- Redirect the 404 error: Redirecting users to another relevant page is the easiest way to fix 404 errors on your site. Just make sure you redirect them to something relevant — don’t just send them back to your homepage.
- Restore the page: If you find there’s still a lot of demand for a page you’ve deleted and there’s no suitable page to redirect users to, consider restoring the original page.
- Correct the link: If broken links exist on your site, you can simply edit the link to point to the correct URL. You won’t be able to fix links on websites you don’t control, however.
- Create a 404 page: By creating a custom 404 error page, you can make sure no visit is wasted—more on this below.
If you have a lot of 404 errors, you’ll need to prioritize your efforts. If you have 404 errors on any major pages, fix these first. Product pages, contact pages, and service pages with 404 errors should be fixed first.
Other pages may not be so pressing. Google Search Console may uncover 404 errors on pages that a human user would never be able to navigate to. You’ll want to fix them eventually, but these errors shouldn’t impact your rankings too much.
Find and Fixing 404 Errors on Your WordPress Site
If you have a WordPress site, you can use the same steps above to find 404 errors.
Found them? Great, now let’s fix 404 errors in WordPress.
If you’re getting site-wide errors, it’s probably an issue with your permalinks. Head to “Settings → Permalinks to update your settings.
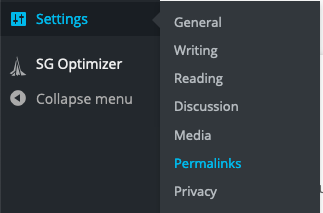
Click “Save Changes” at the bottom of the page once you’re done.
If specific pages are returning 404 errors, you’ll want to set up a 301 redirect for them. WordPress will try to do this automatically, but sometimes it doesn’t work.
The easiest way to do it yourself is by getting Yoast Premium or installing the Redirection plugin.
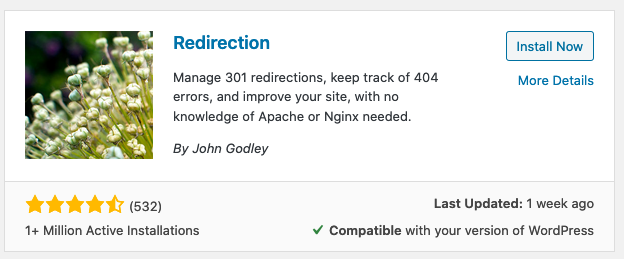
Once it’s installed and activated, head to Tools → Redirection.
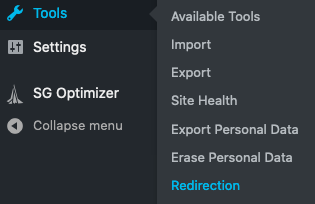
You’ll need to answer a few quick questions to set up the tool.
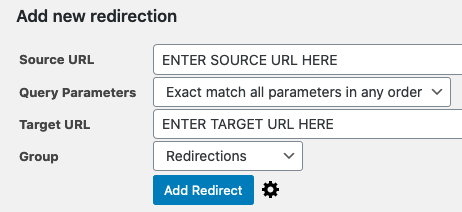
Then you’ll be able to redirect any URL on your WordPress site. Just enter the URL you want to redirect in the Source URL field and the URL you want to redirect the page to in the Target URL field.
Then click Add Redirect.
If this seems confusing or complicated, it might be best to have a website developer or your website hosting support team help you with this to make sure all 404s are redirected properly.
How Often Should You Check for 404 Errors?
How often you should check for 404 errors depends on the size of your site.
Smaller sites with less than 50 pages can probably check for 404 errors every month or so. Larger sites may want to run checks for 404 errors every week or every other day.
Other Top Tools to Find and Fix 404 Errors
The methods I’ve mentioned above aren’t the only ways to find and fix 404 errors. Here are some of the other leading tools you can use.
Dead Link Checker
Dead Link Checker is similar to Screaming Frog. You can use it to check up to 2000 links on your site to see if any are broken.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics doesn’t track 404 errors out of the box, but you can use it to find 404 errors if you have a custom 404 page.
Start by finding the name of your 404 page.

Mine is Page not found – Neil Patel.
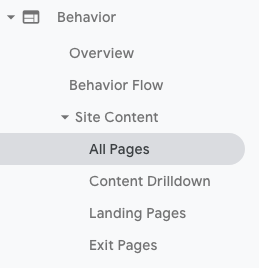
Then open Google Analytics and head to Behavior → Site Content → All Pages
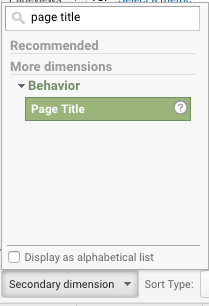
Now add Page Title as a Secondary Dimension.
Click Advanced next to the search bar, then change the rule from Page to Page Title and type your 404 page title into the Containing box.
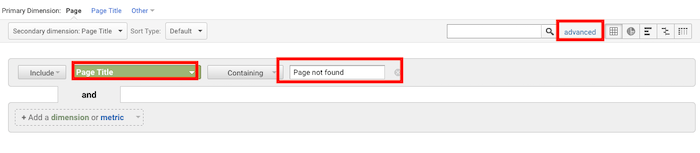
You’ll now have a report of how many people landed on your 404 page, and where they came from.
MonsterInsights
If you have a WordPress site, MonsterInsights can do all of the hard work for you. Rather than creating a manual report in Google Analytics, simply install the MonsterInsights plug-in.
It automatically tracks your 404 errors as soon as you connect your Google Analytics.
Crafting a Unique 404 Error Code Page
I highly recommend creating a unique 404 error code page for your site.
Most standard 404 error messages are way too technical for the average user to understand, and they don’t help them find another relevant page.
With a unique 404 page, you can provide more value to your users and even help them find the information they are looking for.
You can also boost your branding and marketing efforts.
Many companies use a custom 404 error page to reinforce their brand image and inject a bit of humor. Creating a custom URL page also makes it easier to track 404 errors in Google Analytics.
Don’t go overboard, however. A clean and straightforward 404 page is much more effective than an overly elaborate one.
Make sure you include a 404 header status on your custom page, too.
If you don’t, search engines won’t recognize the page correctly. Google will keep displaying the page in search results and send you a deluge of soft 404 error messages in the Search Console.
If you need some inspiration, here are some of my favorite unique 404 page examples:
Airbnb
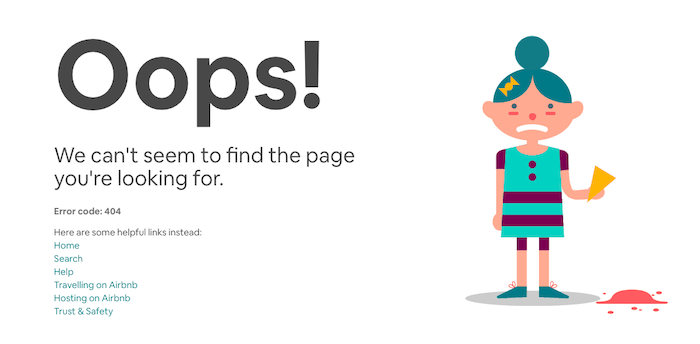
Airbnb makes the most of a 404 error by showing users a fun GIF and offering links to their site’s main pages.
Southwest
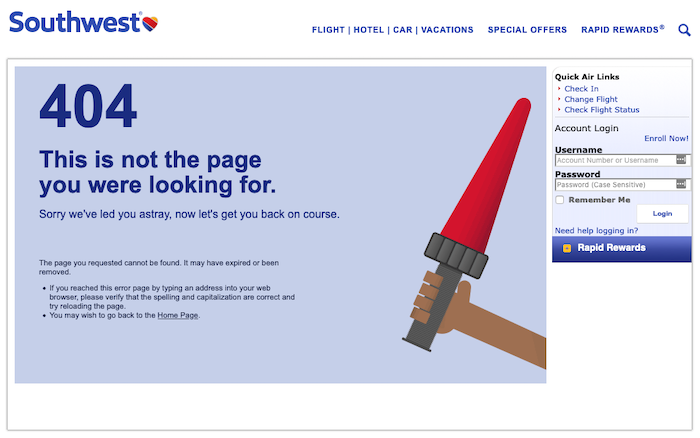
Southwest takes full responsibility for the mistake and explains how it may have happened if users want to try to find the page again.
Wendys

Wendys goes above and beyond with their 404 page. There are no links to other parts of their site here; just a free game users can play to pass the time.
Conclusion
If you have a website, 404 errors are inevitable. But there’s no reason to let them damage your site’s user experience and hurt your rankings.
Use the strategies and tools above to regularly run checks to find 404 errors and fix them quickly. The faster you fix them, the less damage they can do.
How many 404 errors have you been able to fix on your site? Let me know in the comments.
The post How to Find and Fix 404 Errors appeared first on Neil Patel.
from Blog – Neil Patel https://ift.tt/323VkAc
via IFTTT
